🚀 Accelerate Through GM's 2023 Financial Landscape Like a Pro! 📊
GM (General Motors) 2023 Beginner’s Guide Introduction:
Hello, up-and-coming finance enthusiasts! Are you ready to shift gears and delve into the financial mechanics of General Motors in 2023? Introducing "GM (General Motors) 2023: Beginner's Guide to Financial Analysis," your premier guide from Quality Business Consultant, crafted by the finance expert Paul Borosky, MBA. This guide isn't just a rundown of numbers; it's your roadmap to navigating the fiscal intricacies of one of the automotive industry's leaders!
Why You'll Love This Guide:
- Guided by a Finance Expert: 🎓 Cruise through GM's financials with Paul Borosky, MBA, your experienced navigator from Quality Business Consultant.
- Detailed Financial Exploration of GM: 📉 Get under the hood with GM's income statements and balance sheets for 2023, revealing the company's financial engine.
- Comprehensive Financial Ratio Analysis: 🧮 Decode over twenty essential financial ratios to understand GM's fiscal performance and stability.
- Demystifying Financial Terms: 📚 Our "In other words" segments simplify complex financial terminology, making it accessible and engaging.
- Customized Analysis Techniques: 💡 Apply Paul's targeted analysis tips to enhance your financial analysis skill set, whether for academia or the boardroom.
- Further Insights with Detailed Report: 🔍 Dive deeper with our "Financial Analysis & Report" for an in-depth look at GM, integrating AI-driven insights with Paul Borosky's expert scrutiny.
Guide Highlights:
- A reader-friendly Legal Disclaimer.
- An enticing Forward to ignite your financial curiosity.
- Thorough breakdowns of Income Statements and Balance Sheets for 2023.
- A deep dive into Financial Ratios, fueling your analytical journey.
- A wealth of financial insights waiting to be explored!
Table of Contents Sneak Peek:
- Exploring Income Statements: Analyzing revenue, costs, and the finer details
- Balance Sheet Breakdown: Dissecting assets, liabilities, and equity – the core components of financial health
- Mastering Financial Ratios: Arming you with the tools to assess GM's financial dynamics
Who's This For?
Tailored for ambitious business students and emerging entrepreneurs, this guide is your fast lane to mastering financial analysis with a focus on General Motors.
Claim Your Guide:
Rev up your financial literacy with "GM (General Motors) 2023: Beginner's Guide to Financial Analysis." Turn the complex world of financial statements into your strategic asset.
Additional Note: This beginner's guide is designed to provide a solid foundation in key financial principles, focusing on income statements, balance sheets, and crucial financial ratios for their analysis. It presents a summarized version of GM's financials, offering specific data, calculations, and ratios to guide your analysis. While the guide equips you with the analytical tools, the deeper financial exploration is yours to undertake. For those seeking a comprehensive, company-specific financial analysis, our "Financial Analysis & Report" offers detailed insights, merging AI technology with Paul Borosky, MBA's experienced evaluation.
Sincerely,
Paul, MBA.
PDF/Downloadable Versions

Click Below for the CURRENT
Downloadable PDF Price!!

Click Below for the CURRENT
Downloadable PDF Price!!
Sample Financial Report

General Motors (GM): Brief Summary
General Motors (GM) is a renowned automotive manufacturer in Detroit, Michigan. With a rich history spanning decades, GM has established itself as a leading car and truck producer, catering to domestic and international markets. The company’s expertise lies in its ability to craft innovative designs, manufacture high-quality vehicles, facilitate sales, and provide financing options.
GM boasts an impressive portfolio of popular brands that have captivated consumers worldwide. These include Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, GMC, and Wuling, each offering a unique blend of style, performance, and reliability. These brands represent GM’s commitment to delivering exceptional vehicles across diverse segments, catering to customers’ needs and preferences.
A Legacy of Excellence
GM’s enduring legacy in the automotive industry can be attributed to its unwavering dedication to excellence. By combining cutting-edge technology with meticulous craftsmanship, the company has consistently produced vehicles that redefine industry standards. From sleek sedans to robust trucks, GM’s diverse lineup showcases its commitment to innovation, safety, and customer satisfaction.
Global Reach and Impact
With a strong presence in the United States and worldwide, GM has successfully expanded its operations to cater to a global customer base. The company has established itself as a critical player in the international automotive market by strategically leveraging its vast manufacturing facilities, distribution channels, and dealerships. GM’s commitment to sustainability and environmental stewardship further highlights its aim to contribute positively to the communities it serves.
From a financial perspective, GM’s stock price has fluctuated between $30.33 and $67.21 in the last 52 weeks, ending August 2022. The company’s last dividend payment was $0.38 back in March 2020. The market capitalization rate for the company is approximately $57.739 billion. As for the beta, it is 1.28. This shows that the firm is moderately more risky of an investment than the overall market.
General Motors (GM) Financial Report Sources
“General Motors (GM) 2019 Financial Report: Financial Statements and Financial Ratios: Defined, Discussed, and Analyzed for 5 Years” was written by Paul Borosky, MBA., and owner of Quality Business Plan. In this report, I used GM’s 2018 10k, GM’s 2017 10k annual report, 2016 10k annual report, 2015 10k annual report, and GM’s 2019 10k annual report as the basis for information gathering.
Section 1: General Motors (GM) Income Statement Analyzed
In this section, I walk through a broad definition of what an income statement is and why it is essential. I then discuss and define income statement line items, such as revenues, gross profits, etc., in detail. After each line item is defined and discussed, I finally offer a summary analysis of GM’s significant income statement line item trends from 2015 to 2019 in most cases.
The Importance of Income Statement for General Motors (GM) Financial Analysis
Assessing Performance and Profitability
The income statement is vital in analyzing General Motors’ financial health. It provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period. Analysts can evaluate GM’s performance and profitability by examining this statement, allowing for informed decision-making.
The income statement helps stakeholders understand GM’s revenue sources, such as car and truck sales, financing activities, and aftermarket services. It also reveals the company’s expenses, including manufacturing, marketing, and research and development investments. Analysts can assess GM’s ability to generate profit and its cost management strategies by comparing revenue and expenses.
Identifying Trends and Financial Stability
The income statement lets analysts identify trends and patterns in GM’s financial performance. By examining year-on-year or quarter-on-quarter data, analysts can evaluate growth rates, identify potential areas of concern, and recognize opportunities for improvement. This analysis provides insights into GM’s financial stability and ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
Additionally, the income statement helps in ratio analysis. The income statement can derive key financial ratios like gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. These ratios provide valuable insights into GM’s operational efficiency, cost control measures, and profitability.
Sample: GM Revenue Growth.
General Motors ended 2015 with revenues of approximately $135.7 billion. The following year, the company would increase revenues to approximately $149 billion. However, revenues fluctuated over the next three years from $147 billion to $137.2 billion in 2019. This trend indicates that the organization is having difficulty attracting and retaining loyal customers in the automobile market. On average, GM’s growth rate was .5%. For a mature company, this would be slightly below average for growth. From an investor’s perspective, this would be a little bit concerning. I mean, $137 billion is a lot of money. However, this is significantly lower than in the previous three years.
GM (General Motors) 2023 Summary Income Statement |
|||||
| Column1 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 |
| Revenues | 171,842 | 156,735 | 127,004 | 122,485 | 137,237 |
| COGS | 141,330 | 126,892 | 100,544 | 97,539 | 110,651 |
| Gross Profit | 30,512 | 29,843 | 26,460 | 24,946 | 26,586 |
| SG&A | 9,840 | 10,667 | 8,554 | 7,038 | 8,491 |
| Depreciation | 11,888 | 11,290 | 12,052 | 12,815 | 14,118 |
| R & D | - | - | - | - | - |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total Operating Expenses | 162,544 | 146,421 | 117,680 | 115,851 | 131,756 |
| EBIT | 9,298 | 10,315 | 9,324 | 6,634 | 5,481 |
| Other Income | - | - | - | - | - |
| Interest Expense | 911 | 987 | 950 | 1,098 | 782 |
| EBT | 10,403 | 11,597 | 12,716 | 8,095 | 7,436 |
| Taxes | 563 | 1,888 | 2,771 | 1,774 | 769 |
| Net Income | 9,840 | 9,708 | 9,945 | 6,427 | 6,732 |
Section 2: GM Balance Sheet Analyzed
For GM’s balance sheet, I again review each critical line item from the balance sheet. In reviewing each line item, I will define GM’s balance sheet line items, such as cash, property, plant and equipment, and liabilities. Next, I will offer a summary analysis of GM’s essential balance sheet line items.
The Importance of Balance Sheet for General Motors (GM) Financial Analysis
Assessing Financial Position and Liquidity
The balance sheet is crucial in analyzing General Motors’ financial health. It provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder’s equity at a specific time. Analysts can assess GM’s financial position and liquidity by examining the balance sheet, enabling a comprehensive evaluation.
The balance sheet showcases GM’s assets, including cash, inventory, property, plant, and equipment. It also presents liabilities such as debts, accounts payable, and accrued expenses. Analysts can gauge GM’s ability to meet short-term and long-term obligations by comparing assets and liabilities and evaluating the company’s liquidity position.
Evaluating Capital Structure and Solvency
The balance sheet helps analysts evaluate GM’s capital structure and solvency. Shareholders’ equity represents the company’s net worth and is a crucial balance sheet component. It highlights the portion of GM’s assets financed by shareholders’ investments and retained earnings. This information assists in understanding the company’s financial leverage and ability to sustain operations in the long run.
Additionally, the balance sheet aids in assessing GM’s solvency, as it reveals the proportion of the company’s assets financed by external sources, such as debts and loans. Analysts can gauge the company’s ability to manage its debts and meet financial obligations by examining debt-to-equity ratios and maturity profiles.
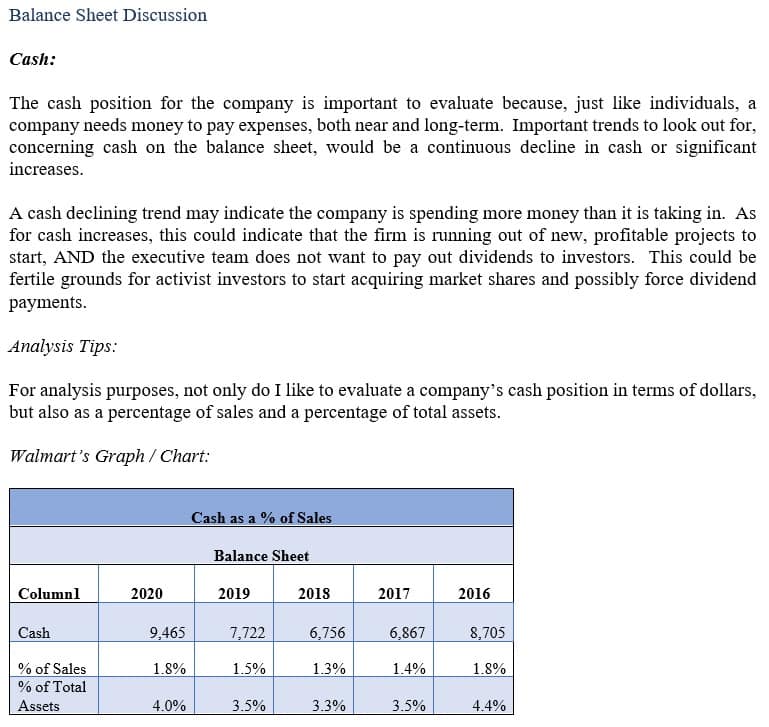
GM’s Cash Position.
General Motors ended 2015 with approximately $15.2 billion in cash. The following year, the cash position would fall to $12.6 billion. However, in the next several years, their cash position would climb to $19 billion in 2019. The cash position growth indicates that the firm needs more liquid assets to fund operations. As compared to total assets, cash is approximately 8.4%. Finally, as a percentage of sales, this would be 13.9%.
GM (General Motors) 2023 Summary Balance Sheet |
|||||
| Column1 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 |
| Cash | 18,853 | 19,153 | 20,067 | 19,992 | 19,069 |
| Short Term Investment | 7,613 | 12,150 | 8,609 | 9,046 | 4,174 |
| Account Receivable | 12,378 | 13,333 | 7,394 | 34,244 | 33,398 |
| Inventory | 16,461 | 15,366 | 12,988 | 10,235 | 10,398 |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - |
| Current Assets | 101,618 | 100,451 | 82,103 | 80,924 | 74,992 |
| Net PPE | 50,321 | 45,248 | 41,115 | 37,632 | 38,750 |
| Goodwill | 4,862 | 4,945 | 5,087 | 5,230 | 5,337 |
| Other | - | - | - | ||
| Total Assets | 273,064 | 264,037 | 244,718 | 235,194 | 228,037 |
| Accounts Payable | 28,114 | 27,486 | 20,391 | 19,928 | 21,018 |
| Accrued Expense | 27,364 | 24,910 | 20,297 | 23,069 | 26,487 |
| Accrued Taxes | - | - | - | - | - |
| Notes Payable | - | - | - | - | - |
| LT Debt - Current | 38,540 | 36,819 | 33,720 | 36,913 | 37,400 |
| Other | - | - | |||
| Total Current Liabilities | 94,445 | 91,173 | 74,408 | 79,910 | 84,905 |
| LT Debt | 82,773 | 75,921 | 75,659 | 72,981 | 65,924 |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total Liabilities | 204,757 | 191,752 | 178,903 | 185,517 | 182,080 |
| Common Stock | 19,142 | 26,442 | 27,076 | 26,556 | 26,074 |
| Treasury | - | - | - | - | - |
| Retained Earnings | 55,391 | 49,251 | 41,937 | 31,962 | 26,860 |
| Other | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total Equity | 68,189 | 71,927 | 65,815 | 49,677 | 45,957 |
| Total Equity & Liability | 273,064 | 264,037 | 244,718 | 235,194 | 228,037 |
Section 3: General Motors (GM) Financial Ratios Analyzed
For this section, I have chosen several financial ratios for GM to review. In reviewing each of GM’s financial ratios, I first start by defining the financial ratio. Next, I supply the financial formula for calculating the specific ratio. Finally, I briefly analyze General Motors’ Important Financial ratios.

GM Current Ratio:
General Motors’ current ratio ended 2015 at 1.09. The company was well-balanced in this position because it had slightly more current assets than current liabilities. Over the next several years, the organization’s current ratio would fall to .88 in 2019. This indicates that the company continually increases its current liabilities compared to current assets. In doing this, the firm is continually increasing its risk for insolvency. In some industries, such as retail, having a current ratio below 1.0 is acceptable because of the continuous cash flow. In GM’s case, a current ratio below 1.0 for a sustained period is probably a risk the organization should not take.
GM Total Asset Turnover:
GM ended 2015 with a total asset turnover of .70. In the next five years, the company’s total asset turnover would fall to .60. This continued decline in total asset turnover shows that the firm is utilizing assets in the company. The main driver for this problem would be its fixed assets. This ratio has also been continually declining in reviewing the fixed asset turnover. This means that the firm is not optimally using its plants and equipment. To improve the fixed and total asset turnover, the company must decide which plant and equipment are underutilized and divest the property accordingly.
GM Return on Assets:
GM’s return on assets ended in 2015 at 4.94%. In the next four years, the return assets would fall to 2.92. This means that the company is making less money on management-controlled assets. To improve this issue, GM’s executive team needs to identify which assets may be divested. Or, even better, identify how the company can improve sales while maintaining the status quo on assets held.
GM Debt ratio.
General Motors’ debt ratio is relatively low. Starting in 2015, its debt ratio was 22.4%. In the next three years, their debt ratio would continually climb until it reached 32.1% in 2018. However, in 2019, General Motors lowered its debt ratio back to 28.9%. Most large organizations tend to have significant debt as compared to equity. The organization can make money on borrowed money by having a prominent debt position.
Further, the companies can exploit tax benefits for interest payments made. A benefit of General Motors’ low debt ratio is that they are better positioned to weather recessionary times. A challenge is that the company needs more equity to maintain operations and have any future growth opportunities.
The Importance of Financial Ratios for General Motors (GM) Financial Analysis
Assessing Performance and Efficiency
Financial ratios play a vital role in analyzing General Motors’ financial health. These ratios provide valuable insights into the company’s performance, efficiency, and profitability. Analysts can better understand GM’s financial position and make informed decisions by examining these metrics.

Financial ratios such as return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), and return on investment (ROI) help assess GM’s ability to generate profits from its assets and investments. These ratios provide a measure of the company’s operational efficiency and its ability to utilize resources effectively.
Evaluating Financial Stability and Risk
Financial ratios also aid in evaluating GM’s financial stability and risk management. Ratios such as debt-to-equity ratio, current ratio, and interest coverage ratio provide insights into the company’s leverage, liquidity, and ability to meet its financial obligations. These ratios help assess GM’s solvency and capacity to handle financial risks.
Furthermore, ratios like gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin reveal GM’s profitability and cost management efficiency. These metrics enable analysts to compare GM’s profitability against industry benchmarks and identify areas for improvement.